The Benefits Of Using A Heat Pump System
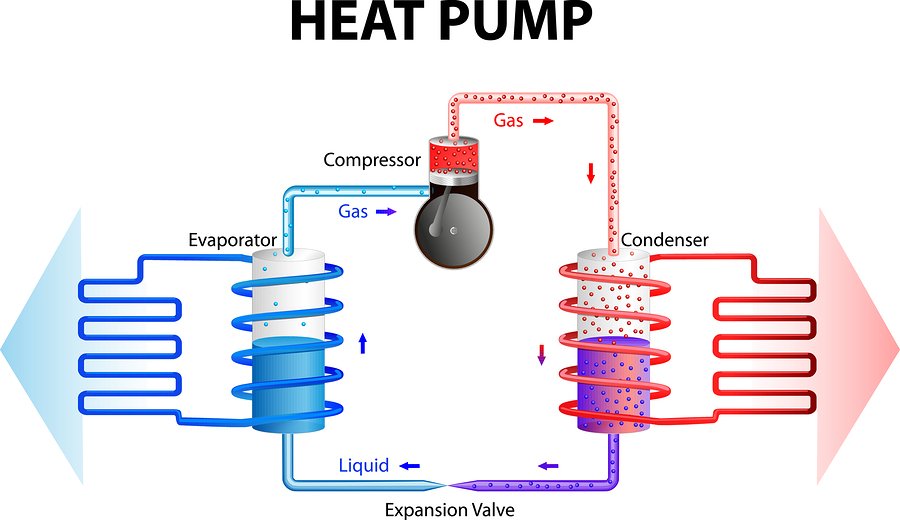
In many areas around the country where the climate is relatively moderate, a heat pump system is energy-efficient and a cost-effective alternative to using traditional furnaces or air conditioners. Similar to how a refrigerator works, a heat pump uses electric power to force heat coming from a cool place into a warm space.
During winter, the heat pump works by pushing heat coming from cold outdoors to keep the inside of your home warm. Conversely, the heat pump pushes heat from inside the home outdoors during summer. This working principle of moving heat from one place to another makes heat pumps operate at a quarter of the cost of traditional cooling and heating appliances. A heat pump system has three types:
- Air-To-Air
- Water Source
- Geothermal
In this article, we will discuss these types of heat pumps and their individual features.
What Is A Geothermal Heat Pump
A geothermal heat pump system uses heat coming from the ground instead of air temperature as an exchange medium. Despite the seasonal climate in most parts of the country, at a certain depth underground, the temperature is constant. This underground temperature is warmer than outdoor air during winter and colder during summer. A heat pump takes advantage of this constant temperature by using a heat exchanger.
A heat pump system using a ground or geothermal source is capable of heating, cooling, and even providing hot water for households. There are geothermal heat pumps with variable fan speed and two-speed compressors which provide better indoor comfort as well as energy efficiency and savings. Different types of geothermal heat pump systems include:
- Closed-Loop Systems
- Horizontal
- Vertical
- Pond/Lake
- Open-Loop System
Compared with air-source heat pumps, geothermal heat pumps are relatively quieter, have low maintenance, have a longer life span, and are not affected by outdoor air temperature. This type of heat pump system is more expensive to install, but you can recoup the upfront cost through energy savings after 5 to 10 years of use. The estimated lifespan of a geothermal heat pump is 25 years for internal components and more than 50 years for above-ground elements.
What Is A Water Source For A Heat Pump
A water source heat pump is not an option readily available to everyone. Since you will use water for heat exchange, it is feasible for homes near bodies of water such as ponds, lakes, wells, or any other natural water source. A water source heat pump operates using the same principle by cycling water through a network of pipes installed at the bottom of the water source. Through the cycling process, the pump harnesses heat coming from the water and carries it to the house.
The cooling process works in the same manner by reversing the result. Water source heat pumps are more efficient in cooling homes rather than heating. This option is an excellent alternative to traditional cooling systems if you live in an area with a moderate climate. The main limitation of a water source heat pump is the availability of a natural water source.
What Is An Air Source For A Heat Pump
Air-source heat pumps are standard in many areas of the US, especially in areas with milder winters. The primary benefit of using an air source heat pump system is the efficient method of heating and cooling at a fraction of the cost. In recent years, advancements in air source heat pump technology have allowed for its adoption even in areas with extreme cold climates. It is not a sufficient alternative for heating a household compared with more traditional heating options. The different types of air-source heat pumps are as follows:
- Ducted
- Ductless
- Short-Run Ducted
- Split
- Packaged
- Multi-Zone
- Single-Zone
An air source heat pump system has a compressor with two copper coils, one placed outside and the other indoors. The copper tubes are also surrounded by aluminum fins that help with heat transfer. When a heat pump is in heating mode, the liquid refrigerant inside the outdoor coils absorbs heat from the air as it turns to gas. When gas refrigerant reaches the indoor coils, it releases heat as it transforms back to liquid. Here are some of the technological advancements to heat pumps that facilitate better heating and cooling capacity.
- Variable speed blowers improve system efficiency and reduce the effects of clogged filters, ductwork, and coils.
- Better coil design.
- Double-speed compressors and better electric motors.
- Grooved copper tubing with increased surface area.
- Thermostatic expansion valves facilitate precision refrigerant flow control.
A properly installed air source heat pump can deliver significant savings annually. You can save as much as $460 every year if you use an air-source heat pump system compared to electric heaters.
What Is A Mini Ssplit Heat Pump & A Ductless Heat Pump
Ductless or mini-split heat pumps are ideal for homes with no existing ductwork. You can retrofit your home with a mini split heat pump using air source heat transfer to augment other heating systems already in place. If you have space heaters, radiant panels, or hydronic heat sources, mini split heat pumps make excellent add-ons.
In some instances, when you need heating or cooling for a room extension, it is more feasible to use mini split heat pump systems rather than extent and retrofit ductwork. Similar to choosing a traditional HVAC unit, you also need to make sure that the mini split heat pump you choose conforms to government-recommended energy-efficiency ratings.
What Are The Benefits Of A Mini Split Heat Pump
Since mini-split heat pump systems are relatively small and compact, there is greater flexibility in terms of zoning. You can use it to cool or heat individual rooms inside your house. There are some models with as many as four indoor handlers you can install in four different areas or rooms while only using a single outdoor unit. You can customize the number of indoor units depending on the requirements of your home. By installing individual thermostats for each zone, you have better control over temperature conditioning; hence, have more energy savings.
A ductless mini split heat pump system is also easier to install. You only need a three-inch hole through a wall to connect the conduit that attaches to the indoor and outdoor units. Manufacturers of this type of heat pump system provide homeowners with a variety of options when it comes to conduit length. This means you can put the outdoor unit as far as 50 feet from the indoor unit.
Since mini-split heat pumps don’t have air ducts, you also minimize energy loss linked to ductwork systems. The energy lost as treated air travels through air ducts accounts for over 30% of your energy consumption.
Mini split systems are also flexible in terms of interior design options. The indoor unit can be mounted onto a ceiling, suspended from a ceiling, or hanging down the wall. There are also floor-standing models available if you are looking for something easier to install.
How To Select A Heat Pump System For Your Home
When choosing a heat pump system for residential use, you need to look at the EnergyGuide label. This pertains to the pump efficiency in heating and cooling. The heating efficiency of a heat pump is expressed by the heating season performance factor (HSPF), while the cooling efficiency is indicated by the seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER). If you live in a warmer climate, focus on getting a heat pump with a higher SEER. On the other hand, if you are looking for a higher heating capacity for cold weather, look for a heat pump with a higher HSPF. Aside from the cooling and heating efficiency of the heat pump, you should also consider the following factors:
- Look for a heat pump with a demand-defrost control feature. This feature minimizes the defrost cycle, which in turn reduces supplementary energy consumption.
- All heat pumps have fans and compressors. These components produce noise, which can be irritating. You should look for a model with a lower sound rating of 7.6 decibels or lower. To further reduce noise, mount the indoor unit in a noise-reduction base.
Aside from these features, you should also look for heat pumps with dual compressors and variable fan speed. These advancements can ensure that you are getting the most out of the pump performance. If you compare a heat pump system with fuel-fired furnaces, this option is highly economical. But remember that heat pumps still use electricity so your savings depend on the comparative cost of using electricity versus other fuel sources such as natural gas.
Are you thinking about getting an air-source heat pump for your home? Talk to a specialist from Fischer Heating today to learn more about your options, or contact us with your questions.
